Solvent Miscibility Chart: The Ultimate Guide You Need
Understanding solvent miscibility is crucial for scientists and engineers alike, and the solvent miscible chart serves as a vital tool for this purpose. A comprehensive solvent miscible chart directly informs the selection process in diverse applications, such as in pharmaceutical formulation. The attributes displayed within a solvent miscible chart greatly enhance understanding of solvent interactions, and directly impact the efficacy of reactions, leading to optimized chemical processes as studied extensively by researchers in institutions such as Dow Chemical Company. Many chromatography methods rely on carefully selected solvents for optimum separation, with the solvent miscible chart helping determine compatibility.
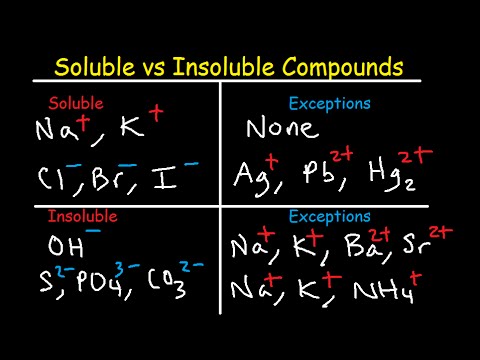
Image taken from the YouTube channel The Organic Chemistry Tutor , from the video titled Soluble and Insoluble Compounds Chart – Solubility Rules Table – List of Salts & Substances .
Structuring Your "Solvent Miscibility Chart: The Ultimate Guide You Need" Article
This guide outlines the optimal structure for an article focused on "solvent miscibility chart," designed to be informative, professional, and easily understood. The layout aims to comprehensively cover the topic, maximizing user understanding and search engine visibility.
Introduction: Defining Miscibility and Its Importance
Start by clearly defining miscibility. This is crucial for readers who may be unfamiliar with the term. Briefly explain that miscibility refers to the ability of two or more substances to mix in all proportions (i.e., to fully dissolve in each other) to form a homogeneous solution. Emphasize the importance of understanding miscibility in various applications, such as:
- Chemical synthesis and reactions
- Formulation of paints, coatings, and adhesives
- Pharmaceutical development
- Cleaning and degreasing processes
- Material science
Introduce the concept of a "solvent miscible chart" as a tool that visually represents which solvents mix well together. State the purpose of the article: to provide a comprehensive understanding of these charts, their interpretation, and practical applications.
What is a Solvent Miscibility Chart?
This section will delve into the specific nature of solvent miscible charts.
Definition and Structure
Define a solvent miscible chart as a matrix or table that shows the compatibility (miscibility) of various solvents with each other. Describe the typical structure of the chart:
- Rows and Columns: Solvents are listed both in rows and columns.
- Cells: The cells at the intersection of each row and column indicate whether the corresponding solvents are miscible or immiscible. This is usually represented by:
- A symbol (e.g., checkmark, "+") indicating miscibility
- A different symbol (e.g., "X", "-") indicating immiscibility
- Sometimes, a third symbol or color to represent partial miscibility.
Types of Solvent Miscibility Charts
Discuss different types of charts, if applicable. For example:
- General Solvent Miscibility Charts: Broad coverage of common solvents.
- Specialized Charts: Focused on specific classes of solvents (e.g., polar solvents, non-polar solvents) or solvents used in particular industries.
- Predictive Charts: Based on solubility parameters and predictive models. Note these are often less reliable than experimental data.
Understanding and Interpreting a Solvent Miscibility Chart
This is the most critical section. Provide detailed guidance on how to use a chart effectively.
Reading a Chart Step-by-Step
Use a numbered list to guide the reader:
- Identify the Solvents of Interest: Locate the two solvents you want to check for miscibility on the chart (one in the row and one in the column).
- Find the Intersection: Trace the row and column of the selected solvents to find the cell where they intersect.
- Interpret the Symbol: Determine whether the symbol in the cell indicates miscibility or immiscibility. Provide clear explanations of what each symbol means (e.g., "+" = miscible at all proportions; "-" = immiscible).
- Consider Temperature: Note that miscibility can be temperature-dependent. Point out that many charts are based on room temperature (typically 20-25°C), and that this should be explicitly stated. A change in temperature can alter miscibility.
Limitations of Solvent Miscibility Charts
Address the limitations of these charts:
- Generalizations: Charts often provide a general indication, but specific conditions (temperature, pressure, presence of other compounds) can affect miscibility.
- Data Sources: The accuracy of the chart depends on the source of the data. Clarify if the chart is based on experimental data or theoretical predictions.
- Binary Systems: Charts usually represent the miscibility of two solvents (binary systems). The presence of a third solvent or other compounds can significantly alter the miscibility.
- Partial Miscibility: The representation of partial miscibility can be subjective and may not provide precise quantitative data.
- Lack of Quantitative Data: Most charts only offer qualitative information (miscible/immiscible) and do not provide quantitative data like solubility limits.
Factors Affecting Solvent Miscibility
Explain the underlying principles that govern miscibility.
Solubility Parameters
Introduce the concept of solubility parameters (e.g., Hildebrand solubility parameter, Hansen solubility parameters). Explain that solvents with similar solubility parameters tend to be miscible. Simplify the explanation to avoid complex mathematical derivations.
Polarity
Explain the role of polarity in miscibility. Emphasize the "like dissolves like" principle:
- Polar solvents (e.g., water, alcohols) tend to be miscible with other polar solvents.
- Non-polar solvents (e.g., hexane, toluene) tend to be miscible with other non-polar solvents.
Hydrogen Bonding
Explain how hydrogen bonding affects miscibility, particularly for solvents containing hydroxyl (-OH) or amino (-NH2) groups.
Molecular Structure and Size
Briefly discuss how the size and shape of solvent molecules can influence miscibility.
Practical Applications of Solvent Miscibility Charts
Provide real-world examples of how solvent miscible charts are used.
Examples
Use bullet points to list diverse applications:
- Developing Solvent Blends: Formulating effective solvent blends for cleaning, coating, or extraction processes.
- Choosing Alternative Solvents: Identifying alternative solvents for reactions or processes based on their miscibility profile.
- Predicting Phase Separation: Predicting potential phase separation issues in multi-solvent systems.
- Optimizing Chemical Reactions: Selecting appropriate solvent combinations to optimize reaction rates and yields.
Case Studies (Optional)
If possible, include brief case studies illustrating the use of a solvent miscible chart in a specific application. For instance, how a chart was used to find a suitable solvent mixture for removing a particular type of contaminant from a surface.
Finding and Using Solvent Miscibility Charts
Explain where readers can find reliable charts and how to properly use them.
Online Resources
Provide links to reputable online databases, chemical suppliers, or academic institutions that offer solvent miscible charts.
Software and Tools
Mention any software tools or online calculators that can be used to predict or assess solvent miscibility based on solubility parameters or other properties.
How to Verify Chart Information
Stress the importance of verifying chart information with experimental data or consulting with experts, especially for critical applications. Remind readers that charts provide a general guideline, and specific experimental testing is often required.
FAQs: Understanding Solvent Miscibility Charts
Have questions about solvent miscibility charts? Here are some common questions and concise answers to help you navigate this useful tool.
What exactly does a solvent miscible chart show?
A solvent miscible chart illustrates which solvents will readily mix together to form a homogenous solution and which will not. It provides a visual representation of solvent compatibility, crucial for various applications like formulating paints, coatings, and cleaning solutions.
How do I interpret a solvent miscible chart?
Typically, a solvent miscible chart uses colors or symbols to indicate miscibility. Solvents marked with a specific color or symbol will mix, while different markers indicate immiscibility. By cross-referencing two solvents on the chart, you can quickly determine if they are compatible.
Why is solvent miscibility important?
Solvent miscibility is essential for ensuring the desired properties and performance of a mixture. If solvents are not miscible, the mixture may separate into layers, leading to inconsistent results or product failure. A solvent miscible chart can help avoid such issues.
Are solvent miscible charts always accurate?
While solvent miscible charts are generally reliable, they are based on ideal conditions. Factors like temperature, pressure, and the presence of other solutes can influence solvent miscibility. Always conduct small-scale tests to confirm compatibility, especially in complex formulations. A solvent miscible chart is a starting point.
So, there you have it! Hopefully, you’ve now got a better handle on using a solvent miscible chart. Keep experimenting, and remember, the solvent miscible chart is your friend!