NG Tube Securement: Avoid Discomfort & Complications Now!
Effective ng tube securement is paramount in patient care, influencing both comfort and treatment efficacy. Hospital settings prioritize securement protocols to mitigate risks associated with tube dislodgement, a common challenge addressed by nursing staff. Proper ng tube securement techniques, often utilizing specialized adhesive products, are essential in preventing complications. The Joint Commission also emphasizes the importance of adhering to established guidelines for ng tube securement, reflecting its significance in maintaining patient safety and minimizing the need for reinsertion procedures.
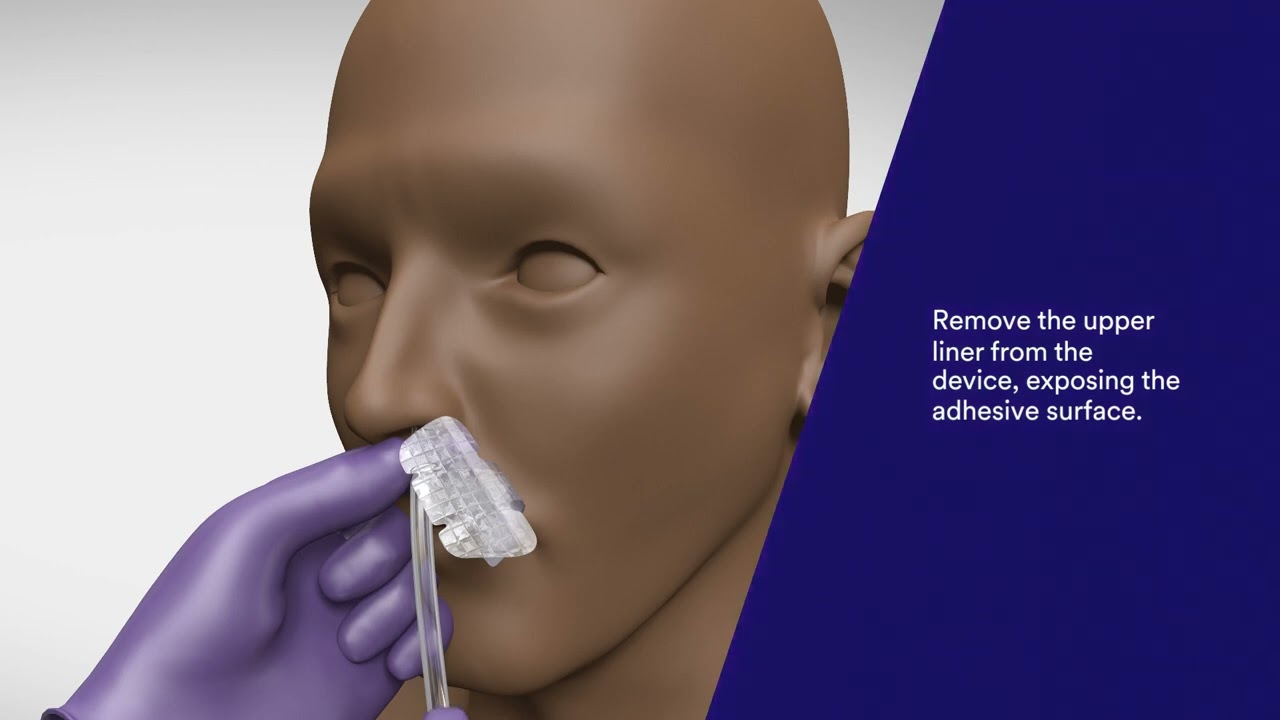
Image taken from the YouTube channel Solventum Medical , from the video titled 3M™ Nasogastric Securement Device Application and Removal Video .
NG Tube Securement: A Guide to Avoiding Discomfort and Complications
Effective NG tube securement is crucial for patient comfort and preventing serious complications. This guide provides a structured approach to understanding and implementing best practices for NG tube securement. The information aims to improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk associated with nasogastric tube use.
Understanding the Importance of Proper NG Tube Securement
Poorly secured NG tubes can lead to a range of issues, from minor skin irritation to more serious complications like accidental dislodgement and aspiration. Therefore, prioritizing proper securement techniques is essential.
Why Proper Securement Matters
- Patient Comfort: A securely fastened tube minimizes movement and friction, reducing irritation and discomfort in the nose and throat.
- Preventing Dislodgement: Securement prevents the tube from being accidentally pulled out, which can be distressing for the patient and require reinsertion.
- Reducing Risk of Aspiration: Dislodgement increases the risk of gastric contents entering the lungs, potentially leading to aspiration pneumonia.
- Maintaining Tube Patency: Securement prevents kinking or twisting of the tube, which can obstruct flow and render the tube ineffective.
- Skin Integrity Preservation: Minimizes pressure and friction on the nasal skin, preventing breakdown and ulceration.
Selecting the Right Securement Method
Several methods exist for securing NG tubes. The best choice depends on individual patient factors, available resources, and clinical judgment.
Types of Securement Devices:
- Adhesive Tape: Traditional method; available in various materials (cloth, paper, transparent film).
- Pros: Inexpensive, readily available.
- Cons: Can cause skin irritation/breakdown, may not provide adequate securement in diaphoretic patients.
- Hydrocolloid-Based Adhesives: Designed to protect skin and promote healing.
- Pros: Gentler on skin, absorbs moisture.
- Cons: More expensive than standard tape, may require additional securement.
- Commercially Available NG Tube Holders/Bridles: Variety of designs, often incorporating soft materials and adjustable straps.
- Pros: More secure, reduce nasal pressure ulcers, easy to reposition.
- Cons: More expensive, some models require specialized training for insertion and maintenance.
- Suture Securement: (Less Common) Involves suturing the NG tube to the nasal septum. Generally used when other methods have failed or are contraindicated. Requires physician order and specialized training.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Method:
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Patient Skin Sensitivity | History of skin allergies, fragile skin (elderly, infants). |
| Patient Diaphoresis | Excessive sweating can compromise adhesive securement. |
| Patient Cognition | Confused or agitated patients may be more likely to dislodge the tube. |
| Tube Size | Larger tubes may require more robust securement. |
| Duration of Use | Long-term use may necessitate more durable and skin-friendly options. |
| Cost/Availability | Institutional budget and availability of specialized securement devices. |
Step-by-Step Guide to Secure NG Tube with Adhesive Tape
This section details the classic method using adhesive tape. Proper technique is essential for effectiveness and patient safety.
Preparing for Securement
- Gather Supplies: Adhesive tape (cloth, paper, or transparent film), skin preparation solution (e.g., benzoin), gloves, scissors.
- Assess Patient: Check for skin integrity, allergies, and level of consciousness. Explain the procedure to the patient.
- Hand Hygiene: Perform thorough hand hygiene.
- Clean and Dry Skin: Gently cleanse the nasal skin with mild soap and water. Pat dry completely.
- Apply Skin Protectant: Apply a thin layer of skin preparation solution (e.g., benzoin) to the nasal skin where the tape will be applied. Allow it to become tacky.
Securement Steps
- Prepare the Tape: Cut two strips of tape, approximately 3-4 inches long. Some practitioners prefer to cut the tape into a "trouser" shape at one end for better adhesion around the tube.
- Apply First Strip: Position the NG tube comfortably along the cheek. Place one end of the first tape strip on the patient’s cheek, close to the nose. Wrap the tape around the NG tube and then back onto the cheek, securing the tube.
- Apply Second Strip: Repeat the process on the opposite side of the nose using the second strip of tape. Ensure the tape is not too tight, which could cause pressure sores.
- Assess Securement: Gently tug on the NG tube to ensure it is securely fastened. Observe the patient’s skin for any signs of irritation or pressure.
- Documentation: Record the date, time, and method of securement in the patient’s chart.
Troubleshooting Common Securement Problems
Even with proper technique, securement challenges can arise. This section provides guidance on addressing common issues.
Addressing Skin Irritation
- Switch to a Gentler Tape: Consider using paper tape or hydrocolloid dressings.
- Use Skin Barrier Wipes/Sprays: These provide a protective layer between the tape and the skin.
- Reposition the Tube: Slight adjustments to the tube’s position can relieve pressure on sensitive areas.
- Monitor Regularly: Assess skin integrity at least every 2-4 hours.
- Consult Wound Care: If skin breakdown occurs, consult a wound care specialist for appropriate management.
Addressing Frequent Dislodgement
- Consider a Different Securement Method: Explore NG tube holders or bridles.
- Ensure Adequate Tape Adhesion: Prepare the skin properly and use fresh tape.
- Evaluate Patient Cognition: For confused patients, consider gentle restraints or increased monitoring (as per facility policy and physician orders).
- Educate the Patient and Family: Explain the importance of not pulling on the tube.
Managing Diaphoresis
- Use Moisture-Absorbing Dressings: Place a thin hydrocolloid dressing under the tape to absorb sweat.
- Consider a Waterproof Tape: Transparent film tape may offer better adhesion in moist environments.
- Change Tape More Frequently: Increase the frequency of tape changes to maintain securement.
- Optimize Environmental Factors: Ensure adequate ventilation and consider using cooling measures to reduce sweating.
Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring is crucial to ensure continued comfort and prevent complications related to NG tube securement.
Key Monitoring Points:
- Skin Assessment: Inspect the nasal skin around the tube at least every 2-4 hours for redness, irritation, or breakdown.
- Tube Position: Verify that the NG tube remains in the correct position by checking the exit mark at the nares.
- Securement Integrity: Assess the integrity of the securement device and replace as needed.
- Patient Comfort: Ask the patient about any discomfort or irritation related to the tube or securement device.
- Tube Patency: Ensure the tube remains patent by regularly flushing it with prescribed solutions.
NG Tube Securement: Frequently Asked Questions
We’ve gathered some common questions about NG tube securement to help you better understand the best practices for comfort and safety.
Why is proper NG tube securement so important?
Proper NG tube securement is critical to prevent accidental dislodgement, reduce irritation to the nasal passages and skin, and minimize the risk of more serious complications like aspiration pneumonia. Securement ensures the tube stays in the correct position for effective feeding or drainage.
What are the key signs of poor NG tube securement?
Signs of poor ng tube securement include redness or skin breakdown around the nostril, frequent pulling or tugging on the tube, increased coughing or gagging, and visible migration of the tube markings. Any of these signs warrant immediate attention.
How often should I check the NG tube securement?
You should check the ng tube securement at least every shift, and more frequently if the patient is restless or agitated. Regular inspection allows for timely adjustments and prevents complications before they arise.
What are some alternative methods for NG tube securement if tape causes skin irritation?
If tape causes skin irritation, consider using hydrocolloid dressings as a base layer or switching to a different type of tape specifically designed for sensitive skin. There are also commercially available NG tube securement devices that can offer a tape-free solution. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best option.
So, that’s the lowdown on ng tube securement! Hopefully, you’ve picked up some tips to make things a little smoother for your patients. Keep those tubes secure, and let’s make patient care a little more comfortable, one securement at a time!