Decode Population Pyramids: Rapid Growth Dynamics & Levronka
Understanding demographic trends is crucial for effective policymaking and resource allocation. Population pyramids, visual representations of age and sex distribution, offer invaluable insights into these trends. Specifically, rapid growth population pyramids: dynamics and implications. Levronka, a model or case study (the exact nature of ‘Levronka’ needs clarification for full accuracy), reveals critical information about potential future societal challenges. The United Nations utilizes population pyramids extensively in its global population projections. Moreover, tools such as GIS (Geographic Information Systems) are often employed to analyze the spatial distribution associated with these demographic structures, aiding in comprehending the drivers behind population growth rates.
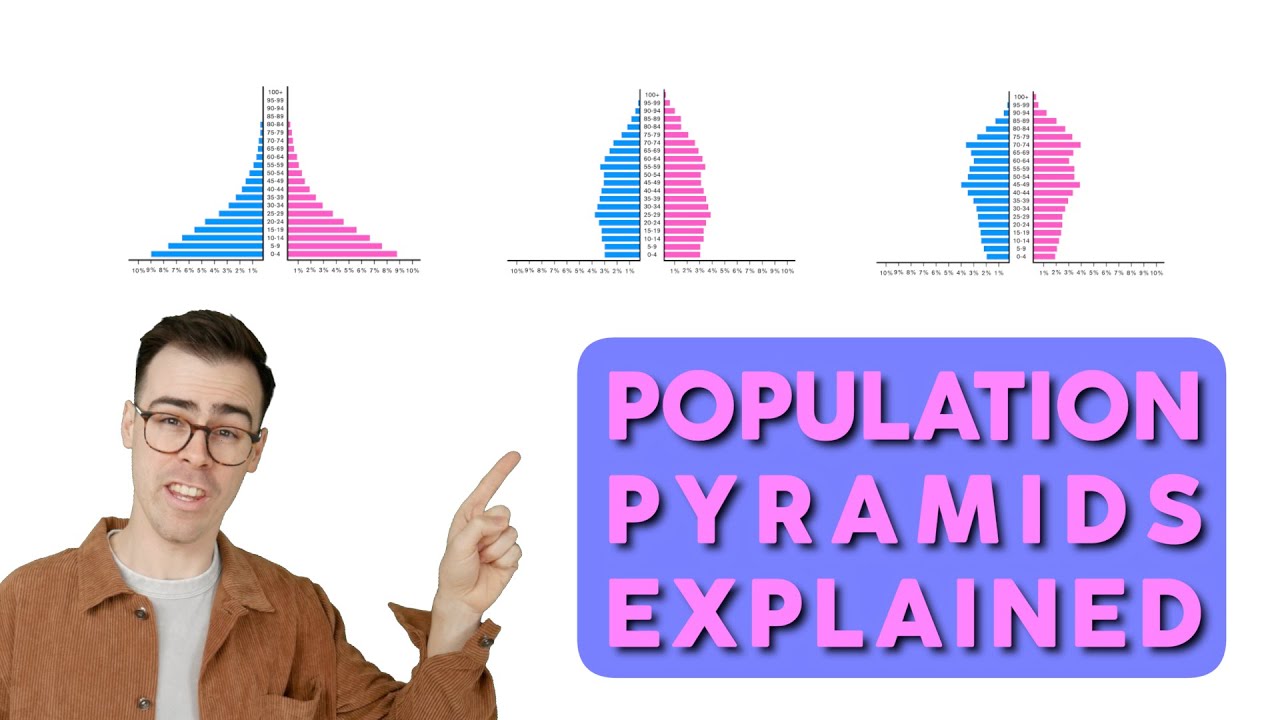
Image taken from the YouTube channel LEARN OR DIE , from the video titled Population Pyramids Explained .
Decoding Population Pyramids: Understanding Rapid Growth, Dynamics, Implications, and the Levronka Case
This article will explore the concept of population pyramids, with a specific focus on understanding the dynamics and implications of rapid population growth, using the term "Levronka" as a fictional example to illustrate key principles. The core objective is to demystify population pyramids and their utility in analyzing demographic trends.
What is a Population Pyramid?
A population pyramid, also known as an age-sex pyramid, is a graphical illustration of the distribution of a population by age groups and sex. It typically consists of two bar graphs, one for males and one for females, placed side-by-side. The vertical axis usually represents age groups, and the horizontal axis represents the percentage or number of individuals in each age group.
How to Read a Population Pyramid
- Shape: The overall shape of the pyramid provides insights into the population’s growth rate and age structure.
- Base: A wide base indicates a high birth rate and a large proportion of young people.
- Apex: A narrow apex suggests a lower life expectancy and a smaller proportion of older people.
- Side Symmetry: Asymmetrical sides can indicate gender-specific mortality rates, migration patterns, or other demographic imbalances.
- Bulges and Indentations: Unusual bulges or indentations can signify past events like baby booms or periods of high mortality (e.g., epidemics or wars).
Rapid Growth Population Pyramids: Characteristics
Rapid growth population pyramids are characterized by a very wide base, indicating a high proportion of young people. The pyramid narrows sharply as you move up the age groups, signifying relatively few older people.
Key Features of Rapid Growth Pyramids:
- High Birth Rate: A defining feature of rapid growth is a high fertility rate.
- Declining Mortality Rates: Improvements in healthcare and sanitation often lead to declining mortality rates, especially among infants and children, contributing to the wide base.
- Young Dependency Ratio: A large proportion of the population is below the working age, leading to a high young dependency ratio (the ratio of dependents to the working-age population).
- Strain on Resources: Rapid growth can put a strain on resources such as education, healthcare, housing, and employment.
Dynamics and Implications of Rapid Population Growth
Understanding the dynamics of rapid population growth is crucial for effective policymaking.
Demographic Dynamics:
- Fertility Rates: High fertility rates are the primary driver of rapid growth. Factors influencing fertility rates include access to contraception, education levels (especially for women), cultural norms, and economic conditions.
- Mortality Rates: Declining mortality rates, especially infant mortality, contribute significantly. Improvements in public health infrastructure, access to clean water, and disease prevention measures are critical.
- Migration: While migration patterns primarily affect the distribution of population rather than the global rate of growth, immigration can contribute to rapid growth in specific regions or countries.
Economic Implications:
- Labor Force: A rapidly growing population can potentially lead to a larger labor force in the future, but this depends on factors such as education and skills development.
- Job Creation: Creating sufficient jobs to accommodate the growing labor force can be a challenge, potentially leading to unemployment or underemployment.
- Economic Growth: While a larger population can increase overall economic output, per capita income may not necessarily increase, particularly if growth is not managed effectively.
Social Implications:
- Education: Providing quality education to a rapidly growing youth population requires significant investment in infrastructure, teacher training, and educational resources.
- Healthcare: Meeting the healthcare needs of a growing population, including maternal and child health services, requires a robust healthcare system.
- Housing: Providing adequate and affordable housing can be a major challenge in areas with rapid population growth.
- Environmental Impact: Rapid population growth can exacerbate environmental problems such as deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution.
Levronka: A Case Study
Let’s imagine a fictional country called "Levronka" experiencing rapid population growth. We’ll use the concept of a population pyramid to understand its demographic situation and the potential challenges it faces.
Levronka’s Population Pyramid (Imaginary)
Imagine Levronka’s population pyramid has a very wide base, signifying a high birth rate. The pyramid narrows quickly as you move up the age groups, indicating a relatively low life expectancy compared to developed nations. There are slight bulges in the 10-14 and 15-19 age cohorts, suggesting a recent increase in birth rates.
Analyzing Levronka’s Situation:
- High Dependency Ratio: Levronka faces a high young dependency ratio, meaning a large proportion of its population is dependent on a smaller working-age population.
- Economic Challenges: The country struggles to provide adequate education, healthcare, and job opportunities for its growing population. Unemployment rates are high among young adults.
- Resource Constraints: Levronka is experiencing water scarcity and deforestation due to the increased demand for resources.
- Potential Opportunities: With strategic investments in education and skills development, Levronka could potentially transform its large youth population into a valuable asset for future economic growth.
- Policy Implications: Levronka’s government needs to focus on policies that promote family planning, improve access to healthcare, invest in education, and create job opportunities. Sustainable development practices are also crucial to mitigate environmental challenges.
Illustrative Data Table (Hypothetical)
The following table shows hypothetical data for Levronka illustrating the population characteristics:
| Demographic Indicator | Value (Levronka) | Value (Global Average) |
|---|---|---|
| Birth Rate (per 1000) | 35 | 18 |
| Death Rate (per 1000) | 8 | 8 |
| Infant Mortality Rate (per 1000) | 40 | 28 |
| Total Fertility Rate | 4.5 | 2.4 |
| Life Expectancy (years) | 65 | 73 |
| Median Age (years) | 20 | 30 |
This table highlights Levronka’s higher birth rate, infant mortality rate, and lower life expectancy compared to the global average, further emphasizing the challenges associated with its rapid population growth.
FAQs: Understanding Population Pyramids and Levronka’s Growth
This section answers common questions about understanding rapid growth population pyramids: dynamics and implications, with a specific focus on the Levronka example.
What is a population pyramid and what does it show?
A population pyramid is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population (typically a country or region). It displays the percentage of males and females in each age group, providing insights into the population’s structure and future growth trends. Examining the shape allows for understanding aspects of rapid growth population pyramids: dynamics and implications.
How does Levronka’s population pyramid indicate rapid growth?
Levronka’s population pyramid, likely characterized by a wide base that rapidly narrows with age, signifies a high birth rate and a large proportion of young people. This structure is a key indicator of rapid population growth and highlights potential demographic challenges and opportunities for Levronka. Understanding rapid growth population pyramids: dynamics and implications in the Levronka case requires analyzing this base.
What are some implications of rapid population growth in Levronka?
Rapid population growth in Levronka can lead to increased demands on resources like education, healthcare, and infrastructure. It may also result in higher unemployment rates and strain on social services. However, it can also create a large workforce and potential for economic growth, provided that effective policies and investments are implemented. Considering rapid growth population pyramids: dynamics and implications, Levronka needs careful planning.
How does the shape of Levronka’s population pyramid affect its future?
The wide base of Levronka’s pyramid means a large cohort will enter their reproductive years, potentially leading to continued high growth unless fertility rates decline. The aging of this population will eventually shift the pyramid’s shape, presenting new challenges like an aging workforce and increased healthcare costs. Predicting this future hinges on an understanding of rapid growth population pyramids: dynamics and implications.
So, there you have it – a peek into the world of rapid growth population pyramids: dynamics and implications. Levronka. Hopefully, you’ve found this helpful and have a better grasp on what these structures can tell us. Now go forth and analyze!