Protostomes vs Deuterostomes: Key Differences Explained
The field of comparative embryology studies development across different animal groups. Body cavity formation, specifically coelom development, differs significantly between protostomes and deuterostomes. Phylogenetic analysis helps classify organisms into these two major groups based on their developmental patterns. Distinguishing between protostomes vs deuterostomes requires understanding that blastopore fate—whether it becomes the mouth or the anus—is a primary characteristic used to differentiate these animal lineages. Understanding the divergence of protostomes vs deuterostomes illuminates the evolutionary history and diversity of the animal kingdom.
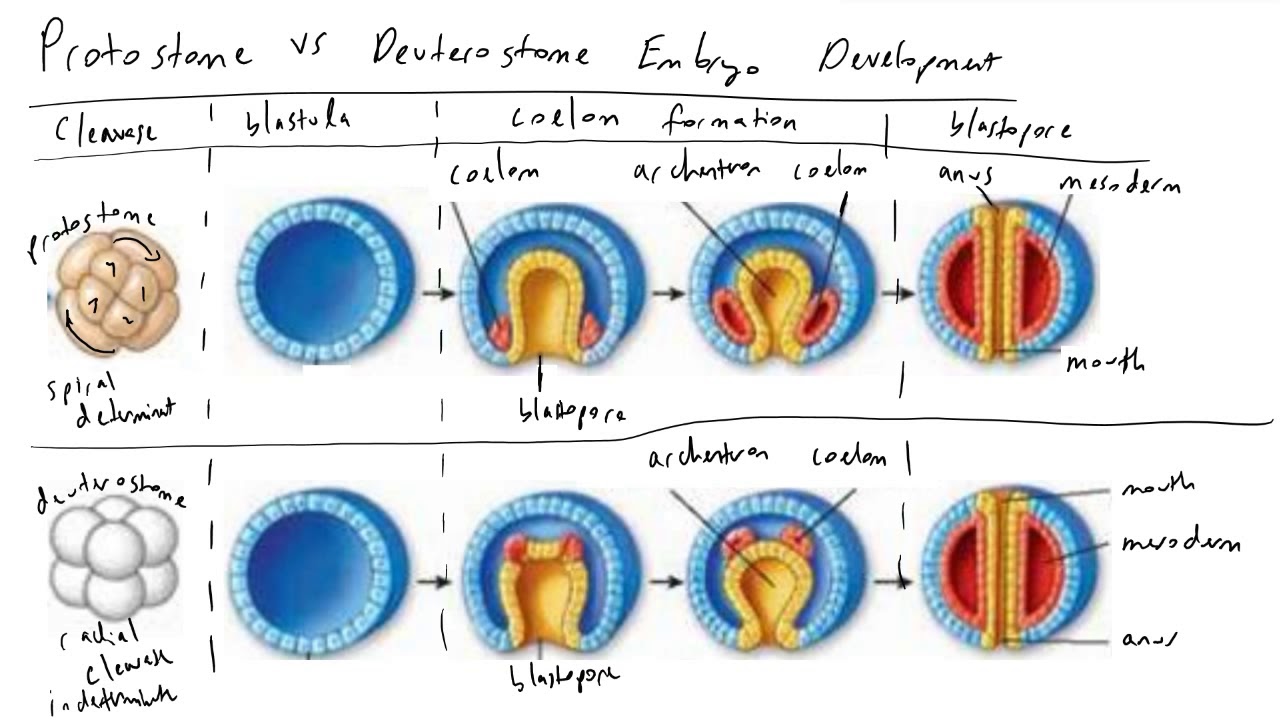
Image taken from the YouTube channel Vincent Stevenson , from the video titled Protostome vs Deuterostome Embryo Development .
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes: Structuring an Informative Article
To effectively explain "protostomes vs deuterostomes", a clear and structured article layout is crucial for reader comprehension. The goal is to present the key differences in an easily digestible format, emphasizing the main keyword throughout.
Introduction: Setting the Stage
The introduction should immediately define both protostomes and deuterostomes in broad terms. You can mention that they are two major groupings of animals based on embryological development. Importantly, highlight that the article will explore the key differences between these two groups.
- Purpose: Introduce the topic and pique reader interest.
- Example sentence: "Protostomes and deuterostomes represent two major branches of the animal kingdom, distinguished primarily by differences in their early embryonic development. This article explores these crucial differences, providing a clear understanding of what sets these two groups apart."
Defining Protostomes and Deuterostomes
This section needs to clearly outline the definitions of each term.
Protostomes Defined
- Explain that the word "protostome" literally means "mouth first."
- Key characteristic: The blastopore (the first opening that forms during gastrulation) develops into the mouth.
- Examples: List common examples of protostomes like insects, mollusks, and annelids.
- Include a brief overview of their evolutionary history (optional).
Deuterostomes Defined
- Explain that the word "deuterostome" means "mouth second."
- Key characteristic: The blastopore develops into the anus. The mouth forms later.
- Examples: List common examples of deuterostomes like echinoderms (starfish) and chordates (including vertebrates).
- Include a brief overview of their evolutionary history (optional).
Key Differences: A Comparative Analysis
This is the core of the article and should be structured for clarity. Consider using a table for a side-by-side comparison, followed by detailed explanations for each point.
Cleavage
- Protostomes:
- Type: Spiral and determinate cleavage.
- Explanation: Explain what spiral cleavage means (cells divide at an angle). Explain what determinate cleavage means (the fate of each cell is determined very early in development).
- Deuterostomes:
- Type: Radial and indeterminate cleavage.
- Explanation: Explain what radial cleavage means (cells divide in a parallel or perpendicular fashion). Explain what indeterminate cleavage means (cells retain the capacity to develop into a complete embryo). This is related to how identical twins can form in deuterostomes.
Coelom Formation
- Protostomes:
- Method: Schizocoelous coelom formation.
- Explanation: Explain that the coelom (body cavity) forms by splitting of the mesoderm.
- Deuterostomes:
- Method: Enterocoelous coelom formation.
- Explanation: Explain that the coelom forms from outpouchings of the archenteron (primitive gut).
Blastopore Fate
- Protostomes:
- Fate: Blastopore becomes the mouth.
- Deuterostomes:
- Fate: Blastopore becomes the anus.
Table Summary
| Feature | Protostomes | Deuterostomes |
|---|---|---|
| Cleavage | Spiral and Determinate | Radial and Indeterminate |
| Coelom Formation | Schizocoelous | Enterocoelous |
| Blastopore Fate | Mouth | Anus |
Evolutionary Significance
(Optional, but recommended for a more comprehensive article)
- Discuss the evolutionary implications of these developmental differences.
- Explain how these differences contribute to the diversity of animal body plans.
- Briefly touch upon the phylogenetic relationships within each group.
Further Exploration
- (Optional) Suggest resources for readers who want to learn more, such as links to academic papers or relevant websites. This adds value to the article.
Protostomes vs Deuterostomes: Frequently Asked Questions
This FAQ section aims to clarify some common questions regarding the key differences between protostomes and deuterostomes, two major divisions within the animal kingdom.
What’s the single most important difference to remember?
The key difference lies in what happens to the blastopore, the first opening formed during embryonic development. In protostomes, the blastopore becomes the mouth. In deuterostomes, the blastopore becomes the anus. This fundamental distinction influences many other developmental processes.
Are humans protostomes or deuterostomes?
Humans, along with other vertebrates like fish, birds, and reptiles, are deuterostomes. This means our anus developed from the blastopore, and our mouth formed later.
Besides the blastopore, what other developmental differences exist between protostomes vs deuterostomes?
Cleavage patterns differ. Protostomes exhibit spiral and determinate cleavage, meaning the fate of early cells is predetermined. Deuterostomes have radial and indeterminate cleavage, allowing for cells to potentially develop into any cell type. Also, protostomes form the coelom by splitting mesoderm while deuterostomes form the coelom by outpocketing of the archenteron.
Can you give some examples of protostomes?
Common examples of protostomes include arthropods (insects, crustaceans, spiders), mollusks (snails, clams, squids), and annelids (segmented worms). Understanding the development of these groups helps to clarify how they differ from deuterostomes.
So, there you have it – a little insight into the fascinating world of protostomes vs deuterostomes! Hopefully, this cleared things up. Now you’re ready to impress your friends (or at least ace that biology quiz!).