PR GL ECG: Accurately Detect Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation, a common cardiac arrhythmia, requires accurate and timely detection for effective management, and early detection of this is really important. The American Heart Association emphasizes the importance of improved diagnostic tools, leading to investigations into methods like pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement. These measurements aim to provide clinicians with precise data for risk stratification and treatment planning. Furthermore, the development of advanced algorithms promises to enhance the reliability and efficiency of pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement. Researchers at the Mayo Clinic contribute significantly to optimizing these techniques, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
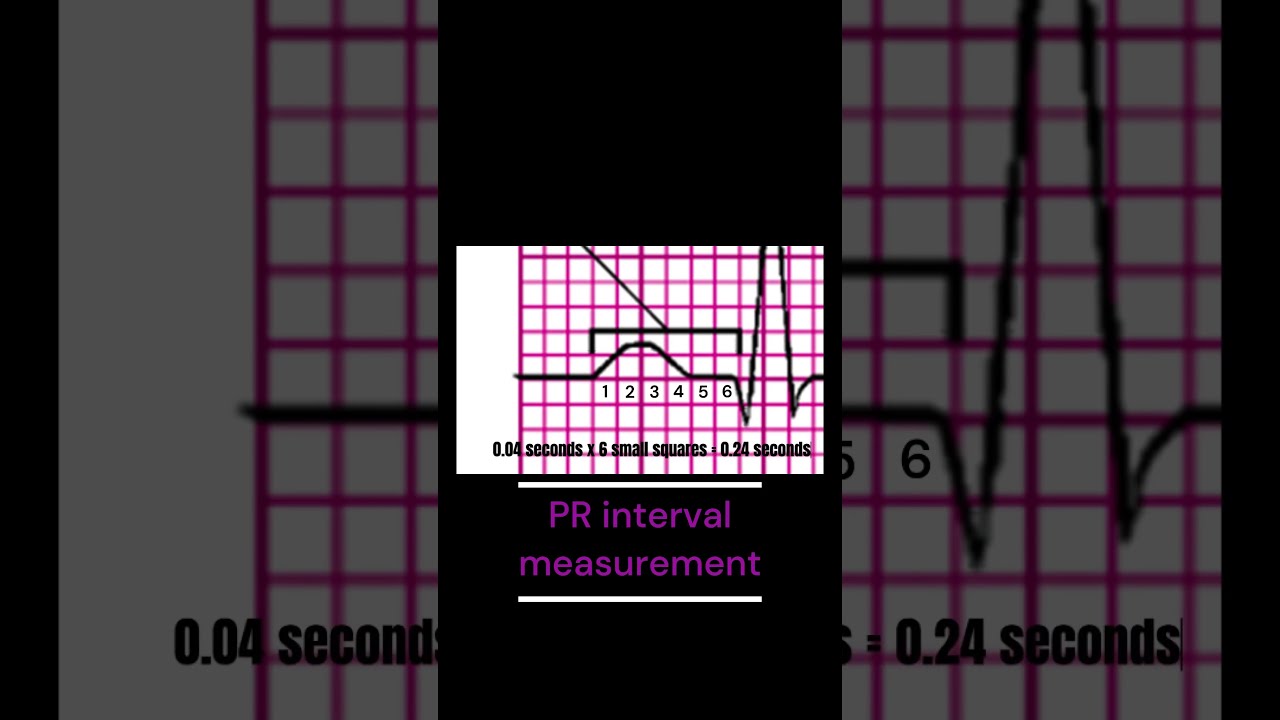
Image taken from the YouTube channel EKG MD , from the video titled How to measure the PR interval .
PR GL ECG and Atrial Fibrillation: A Detailed Look at Accurate Measurement
This article explores the utility of the PR GL ECG – a simplified electrocardiogram (ECG) method using PR interval and GL (likely referring to Global Longitudinal) data – in accurately detecting atrial fibrillation (AFib). We will delve into the principles behind the PR GL ECG, its advantages, limitations, and how it compares to traditional ECG methods for pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation and ECG Basics
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by rapid and irregular beating of the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. This irregular activity can lead to blood clots, stroke, and other heart-related complications. Early detection and management of AFib are crucial.
-
The Role of ECG: An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It provides a visual representation of the heart’s rhythm and can identify abnormalities like AFib. Traditional ECGs typically use multiple electrodes placed on the chest, arms, and legs to capture a comprehensive view of the heart’s electrical activity.
-
Key ECG Components: Understanding certain elements of an ECG tracing is essential for evaluating AFib detection methods. The P wave represents atrial depolarization (electrical activation), the QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, and the T wave represents ventricular repolarization. The PR interval reflects the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
What is PR GL ECG? Exploring the Methodology
The PR GL ECG represents a streamlined approach to ECG monitoring, focusing primarily on the PR interval and potentially incorporating ‘GL’ data. The exact meaning of ‘GL’ needs further clarification but within the context of ECG and cardiac analysis, it likely refers to some global longitudinal measurement, potentially related to strain or electrical activity changes assessed over time.
PR Interval Analysis in AFib Detection
The PR interval can be indicative of underlying atrial activity. In AFib, the absence of consistent P waves due to the chaotic atrial electrical activity can indirectly influence the PR interval’s variability and characteristics. However, relying solely on PR interval changes may not be sufficient for definitive AFib diagnosis.
Potential Role of ‘GL’ (Global Longitudinal) Data
If ‘GL’ represents a global longitudinal measurement, it could potentially reflect changes in overall cardiac electrical activity over time. This longitudinal data, when combined with PR interval measurements, may provide a more comprehensive picture of the heart’s rhythm and potentially improve the accuracy of pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement. The specific algorithms and methodologies employed in using ‘GL’ data with the PR interval are crucial to understanding the effectiveness of this approach. Further research is needed to precisely define the ‘GL’ parameter and its specific contribution.
Simplified Electrode Placement and Data Acquisition
A potential advantage of the PR GL ECG could be a simplified electrode configuration compared to traditional 12-lead ECGs. This could make it easier to implement in remote monitoring settings or for self-monitoring purposes. Fewer electrodes may simplify the acquisition and interpretation of the data.
Advantages and Limitations of PR GL ECG for AFib Detection
Evaluating the benefits and drawbacks is crucial when assessing the viability of pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement.
Potential Advantages
- Simplified Application: The streamlined electrode placement could make it more accessible for use outside of clinical settings.
- Remote Monitoring Potential: Simpler implementation could facilitate remote monitoring of patients at risk for AFib.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Potentially lower cost compared to full 12-lead ECG due to fewer electrodes and simpler analysis.
Limitations
- Accuracy Compared to Traditional ECG: The accuracy of PR GL ECG in detecting AFib needs to be rigorously compared to the gold standard of 12-lead ECG.
- Specificity Challenges: The absence of P waves characteristic of AFib, inferred through PR interval analysis, might not always be specific to AFib, potentially leading to false positives.
- Dependence on ‘GL’ Data Definition: The efficacy is dependent on the precise definition, reliability, and accuracy of the ‘GL’ measurement.
Comparing PR GL ECG with Other AFib Detection Methods
The PR GL ECG needs to be benchmarked against other commonly used AFib detection methods.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12-Lead ECG | Standard diagnostic ECG with 12 electrodes. | Gold standard for AFib diagnosis. | Requires trained professionals for interpretation; less suitable for continuous monitoring. |
| Single-Lead ECG (e.g., KardiaMobile) | Single electrode device recording one ECG lead. | Portable, convenient, FDA-approved for AFib detection in some cases. | Less comprehensive than 12-lead ECG; accuracy may be lower. |
| Wearable Heart Rate Monitors (e.g., Apple Watch) | Uses photoplethysmography (PPG) to detect irregular heart rhythms. | Convenient for continuous monitoring; can alert users to potential AFib. | Prone to false positives; not a replacement for clinical ECG. |
The placement and analysis of the PR GL ECG in this table would depend on further details of the technology. Ideally, clinical validation studies comparing PR GL ECG with these methods are needed to determine its place in AFib detection algorithms.
Future Research and Development
Further research is required to validate the accuracy and reliability of PR GL ECG for pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement. Key areas of focus should include:
- Rigorous Clinical Trials: Conducting large-scale clinical trials comparing PR GL ECG to the gold standard 12-lead ECG.
- Standardization of ‘GL’ Measurement: Clearly defining and standardizing the methodology for obtaining and interpreting the ‘GL’ data.
- Algorithm Optimization: Developing and refining algorithms that accurately analyze PR interval and ‘GL’ data to improve AFib detection accuracy.
- User-Friendliness Studies: Evaluating the usability and practicality of PR GL ECG in real-world settings.
PR GL ECG and Atrial Fibrillation: Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the accuracy and use of PR GL ECG in detecting atrial fibrillation.
How accurate is PR GL ECG in detecting atrial fibrillation?
PR GL ECG technology demonstrates a good level of accuracy in detecting atrial fibrillation. Studies have shown high sensitivity and specificity, meaning it correctly identifies both the presence and absence of the condition. The precise accuracy can vary based on specific implementation and clinical settings, but overall it’s a reliable method for pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement.
What advantages does PR GL ECG offer over traditional ECGs for atrial fibrillation detection?
PR GL ECG often allows for easier and more convenient monitoring compared to traditional ECGs. It can be incorporated into wearable devices, enabling continuous pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement over extended periods. This improves the chances of capturing intermittent episodes of atrial fibrillation that might be missed by standard, short-duration ECG tests.
Can PR GL ECG be used to diagnose all types of atrial fibrillation?
While effective, PR GL ECG might have limitations in diagnosing specific complex arrhythmia cases. It’s primarily designed to detect the presence of atrial fibrillation. If the PR GL ECG atrial fibrillation measurement identifies irregularities, further investigation with more detailed diagnostic tools, like a traditional 12-lead ECG, may be required to determine the specific type of arrhythmia.
Are there any situations where PR GL ECG should not be used for atrial fibrillation detection?
PR GL ECG may not be appropriate for individuals with certain implanted cardiac devices or those with specific pre-existing conditions that could interfere with signal interpretation. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement is suitable and to interpret the results accurately.
So, the next time you hear about pr gl ecg atrial fibrillation measurement, you’ll know a little more about what it’s all about. Hope this helped!