Potassium Atomic Number: The ULTIMATE Guide You NEED!
The element potassium, vital for biological functions, exhibits a fundamental property defined by its potassium atomic number. This specific number, crucial for understanding potassium’s place in the periodic table, dictates its chemical behavior. Comprehending the potassium atomic number is essential for disciplines ranging from chemistry to medicine, influencing everything from understanding ionic bonds to evaluating electrolyte balance.
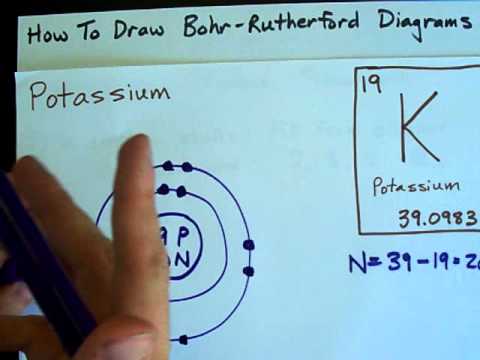
Image taken from the YouTube channel chemistNATE , from the video titled How to Draw Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams – Potassium .
Potassium Atomic Number: The ULTIMATE Guide You NEED! – Layout Explanation
This guide explores the atomic number of potassium. To deliver maximum value to the reader, the article will follow a structure designed to be both informative and easy to understand. The keyword "potassium atomic number" will be strategically incorporated throughout the content to ensure relevance and searchability.
Introduction: Setting the Stage
The introduction should grab the reader’s attention and clearly state what the article is about. It needs to answer the question "Why should I care about the atomic number of potassium?".
- Briefly introduce potassium and its importance in everyday life (e.g., in the body, agriculture).
- State that the article will focus on its atomic number and what that means.
- Mention some key topics to be covered, such as its significance, the element’s place on the periodic table, and related concepts like protons and neutrons.
Defining the Atomic Number
This section lays the foundation for understanding the central topic.
What is an Atomic Number?
- Provide a simple and clear definition of what an atomic number represents. Focus on its role as the identifier of an element.
- Explain that the atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Use analogies if helpful (e.g., comparing the atomic number to a social security number for elements).
Atomic Number vs. Mass Number
- Clearly differentiate between atomic number and mass number. Many readers may confuse these two terms.
- Explain that mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- Include a simple example comparing the atomic number and mass number for potassium (e.g., potassium-39).
-
Use a table to visually highlight the differences:
Feature Atomic Number Mass Number Definition # of Protons # of Protons + Neutrons Symbol Z A Value (Potassium) 19 Varies (e.g., 39, 40, 41)
Potassium: A Closer Look
This section dives specifically into potassium and its properties.
Potassium on the Periodic Table
- Explain where potassium is located on the periodic table (Group 1, alkali metals).
- Describe its position relative to other elements and how its atomic number determines that placement.
- Briefly discuss general trends in the periodic table related to atomic number (e.g., increasing atomic number from left to right and top to bottom).
- Potassium’s symbol (K) and its origin (from the Latin "kalium") should also be explained.
Potassium’s Electronic Configuration
- Briefly explain the electronic configuration of potassium (1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s¹).
- Connect the number of electrons to the atomic number (19 protons necessitate 19 electrons in a neutral atom).
- Discuss the significance of the outermost electron in determining potassium’s reactivity as an alkali metal.
Isotopes of Potassium
- Explain the concept of isotopes (atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons).
- List some common isotopes of potassium, such as potassium-39, potassium-40, and potassium-41.
- Mention the natural abundance of each isotope (e.g., potassium-39 is the most abundant).
- Explain that isotopes of potassium all have the same atomic number (19) but different mass numbers.
The Significance of Potassium’s Atomic Number
This section highlights why knowing the atomic number of potassium is important.
Identifying Potassium
- Reiterate that the atomic number is the defining characteristic of potassium.
- Emphasize that any atom with 19 protons is, by definition, potassium.
Predicting Properties
- Explain how the atomic number helps predict the chemical properties of potassium.
- Link the atomic number to the electronic configuration and reactivity.
Applications in Various Fields
- Briefly describe how knowledge of potassium’s properties (derived from its atomic number) is useful in various fields.
- Examples:
- Medicine: Potassium’s role in nerve function and muscle contraction.
- Agriculture: Potassium as a key nutrient for plant growth.
- Industry: Applications of potassium compounds in manufacturing.
Further Exploration
This section provides ways for readers to learn more.
- Suggest related topics for further reading (e.g., alkali metals, chemical bonding, the periodic table of elements).
- Provide links to reputable sources for more in-depth information (e.g., chemistry textbooks, scientific articles, government websites).
FAQs: Understanding Potassium’s Atomic Number
This FAQ section addresses common questions about potassium’s atomic number and its significance, offering quick answers to help you grasp this fundamental concept.
What exactly is the atomic number of potassium?
The atomic number of potassium is 19. This number defines potassium and indicates that each potassium atom has 19 protons in its nucleus.
Why is knowing the potassium atomic number important?
Knowing the potassium atomic number is crucial because it identifies the element. It distinguishes potassium from all other elements on the periodic table and helps predict its chemical behavior.
Does the number of neutrons in potassium affect its atomic number?
No, the number of neutrons does not affect the atomic number of potassium. The atomic number is solely determined by the number of protons. Different numbers of neutrons create isotopes of potassium, but the atomic number remains constant at 19.
How does potassium’s atomic number relate to its electron configuration?
Because a neutral potassium atom has the same number of electrons as protons, potassium’s atomic number of 19 also indicates it has 19 electrons. This electron configuration dictates how potassium interacts with other elements.
Alright, now you’re armed with some serious knowledge about the potassium atomic number! Hope this helps you crush it in class or just impress your friends at the next science gathering. Go forth and potassium atomic number!