Porencephalic Cyst Radiology: What You Need to Know
Porencephalic cysts, structural abnormalities within the brain, necessitate thorough investigation using advanced neuroimaging techniques. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) protocols play a crucial role in delineating cyst morphology, a key attribute, and differentiating these cysts from other intracranial lesions. Understanding the underlying pathophysiology requires careful consideration of cerebral development processes, with deviations potentially leading to cyst formation. The accurate interpretation of findings is greatly aided by consultation with experienced neuroradiologists who can assess subtle imaging features. The study of porencephalic cyst radiology depends on a solid grasp of neuroanatomy and image modalities.
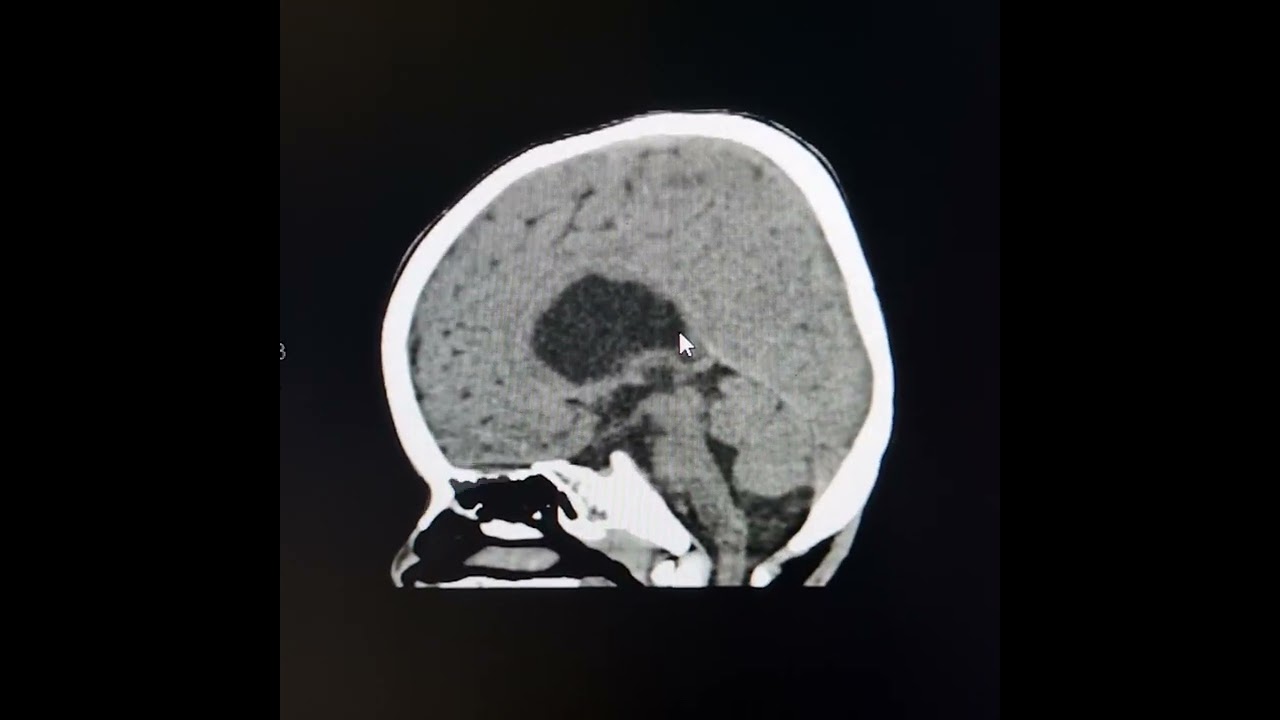
Image taken from the YouTube channel Learning Radiology from CT Scans with Prof Ashraf , from the video titled Porencephalic cysts. .
Porencephalic Cyst Radiology: Optimal Article Layout
This document details an effective article layout designed to inform readers about porencephalic cyst radiology, leveraging the core keyword for search optimization and user engagement. The layout prioritizes clarity, organization, and technical accuracy to provide a valuable resource for those seeking information on this specific neurological condition.
I. Introduction
The introduction should concisely define a porencephalic cyst, its etiology (origin), and briefly introduce the role of radiology in its diagnosis and management. Highlight the importance of accurate radiological assessment.
- Key Points:
- Define "porencephalic cyst" in lay terms.
- Mention the possible causes (e.g., stroke, infection, injury during development).
- State the purpose of the article: to explain radiological evaluation of porencephalic cysts.
II. Imaging Modalities Used in Porencephalic Cyst Radiology
This section focuses on the specific radiological techniques utilized to visualize and characterize porencephalic cysts. Emphasis should be placed on the strengths and limitations of each modality in this context.
A. Computed Tomography (CT)
- Explain the CT technique, including the use of contrast.
- Describe the appearance of porencephalic cysts on CT scans:
- Generally appear as hypodense (darker) areas.
- Often well-defined and CSF-filled (cerebrospinal fluid).
- Discuss the advantages of CT:
- Rapid acquisition time (important in acute settings).
- Good for detecting calcifications or associated hemorrhage.
- Address the limitations:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation.
- Lower soft tissue resolution compared to MRI.
B. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Detail the MRI technique, including various sequences (e.g., T1-weighted, T2-weighted, FLAIR).
- Describe the appearance of porencephalic cysts on MRI:
- T1-weighted: Hypointense (dark).
- T2-weighted: Hyperintense (bright).
- FLAIR: Isointense to CSF (suppressed signal due to fluid attenuation).
- Discuss the advantages of MRI:
- Superior soft tissue resolution.
- Multiplanar imaging capabilities.
- Ability to differentiate cyst contents from surrounding brain tissue.
- Address the limitations:
- Longer acquisition time.
- Contraindications for patients with certain metallic implants.
- Sensitivity to motion artifacts.
C. Ultrasound (Primarily in Infants)
- Explain the role of cranial ultrasound in neonates and infants:
- Can be used to visualize cysts through the fontanelles (soft spots).
- Describe the appearance of porencephalic cysts on ultrasound.
- Discuss the advantages and limitations compared to CT and MRI.
III. Radiological Features of Porencephalic Cysts
This section dives into the specifics of what radiologists look for when evaluating porencephalic cysts on imaging.
A. Location
- Discuss common locations of porencephalic cysts (e.g., parietal lobe, temporal lobe).
- Explain how location can provide clues about the etiology of the cyst.
B. Size and Shape
- Describe the variable sizes and shapes of porencephalic cysts.
- Explain how changes in size over time might be assessed (e.g., serial imaging).
C. Margins
- Explain the importance of evaluating cyst margins.
- Differentiate between smooth, well-defined margins (typical) and irregular margins (potentially indicative of other pathology).
D. Mass Effect
- Define mass effect and its significance.
- Describe how a porencephalic cyst can exert mass effect on surrounding brain structures.
E. Communication with Ventricular System
- Explain whether or not the cyst communicates with the ventricular system or subarachnoid space.
- Discuss the clinical implications of communication.
F. Surrounding Brain Tissue
- Describe the appearance of brain tissue surrounding the cyst (e.g., gliosis – scarring).
- Explain how gliosis may be seen on MRI sequences (e.g., T2-weighted and FLAIR).
IV. Differential Diagnosis
This section outlines other conditions that may mimic porencephalic cysts on imaging.
A. Arachnoid Cyst
- Describe arachnoid cysts and their radiological appearance.
- Explain how to differentiate them from porencephalic cysts (e.g., location, relationship to brain parenchyma).
B. Encephalomalacia
- Explain encephalomalacia (softening of the brain) and its radiological appearance.
- Discuss the key differences that allow differentiation from porencephalic cysts (e.g., less well-defined margins, more diffuse involvement).
C. Schizencephaly
- Describe schizencephaly (a cleft in the brain) and its radiological appearance.
- Explain the differentiating features (e.g., grey matter lining the cleft).
V. Reporting Guidelines for Porencephalic Cyst Radiology
This section provides a structured approach to reporting findings related to porencephalic cysts.
- Identification: Clearly state the presence and location of the cyst.
- Size and Shape: Document the dimensions and general morphology of the cyst.
- Margins: Describe the clarity and regularity of the cyst margins.
- Contents: Indicate the signal characteristics on various MRI sequences (e.g., CSF-like).
- Mass Effect: Assess and describe any evidence of mass effect on surrounding structures.
- Communication: Determine if the cyst communicates with the ventricular system or subarachnoid space.
- Surrounding Brain: Describe the appearance of the adjacent brain parenchyma (e.g., gliosis, atrophy).
- Differential Considerations: Briefly mention possible differential diagnoses.
- Impression: Summarize the findings and offer a diagnostic impression.
VI. Clinical Significance and Management
This section briefly discusses the clinical implications of porencephalic cysts and their management. This part is outside the main keyword "porencephalic cyst radiology" but is important for a complete understanding. This section should primarily focus on the radiologist’s role, as it’s outside the scope of their practice to comment on the entirety of management.
- Neurological Deficits: Link cyst location and size to potential neurological deficits.
- Seizures: Explain the association between porencephalic cysts and seizures.
- Monitoring: Explain the possible recommendation for serial imaging to monitor cyst stability or progression.
- Surgical Considerations: Briefly mention the role of surgical intervention in certain cases.
Porencephalic Cyst Radiology: Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about porencephalic cyst radiology and what you need to know regarding diagnosis and imaging.
What exactly is a porencephalic cyst?
A porencephalic cyst is a fluid-filled cavity in the brain. It often results from injury, stroke, or abnormal brain development. These cysts communicate with the ventricles or the subarachnoid space.
How is a porencephalic cyst typically diagnosed using radiology?
Porencephalic cyst radiology commonly utilizes MRI and CT scans. MRI is often preferred as it provides better soft tissue detail and can help differentiate the cyst from other brain abnormalities. CT scans can be helpful in identifying any associated bone abnormalities.
What are the key things radiologists look for when analyzing porencephalic cyst radiology images?
Radiologists assess the cyst’s size, location, and its relationship to surrounding brain structures. They also look for any signs of mass effect or hydrocephalus. Identifying any underlying cause, such as prior hemorrhage or infarct, is also crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Are there any specific imaging techniques used in porencephalic cyst radiology besides MRI and CT?
While MRI and CT are the primary imaging modalities, ultrasound can sometimes be used in infants to visualize the brain through the fontanelles. Specific MRI sequences, such as FLAIR, can also be particularly helpful in characterizing the fluid within the porencephalic cyst.
And that’s a wrap on porencephalic cyst radiology! Hopefully, you found this helpful and are now a little more confident navigating this complex topic. Best of luck with your further explorations!