Neon Bohr Model Explained: The Ultimate Easy Guide
The Bohr model, a foundational concept in atomic physics, provides a simplified yet insightful framework for understanding atomic structure. Specifically, the neon borhs modle demonstrates electron arrangement within the element neon. Understanding of Quantum Mechanics enables a deeper understanding of the neon borhs modle and its limitations regarding electron placement around the nucleus, with subsequent theories offering refinements. Developed at the Niels Bohr Institute, it visually illustrates the energy levels where electrons reside.
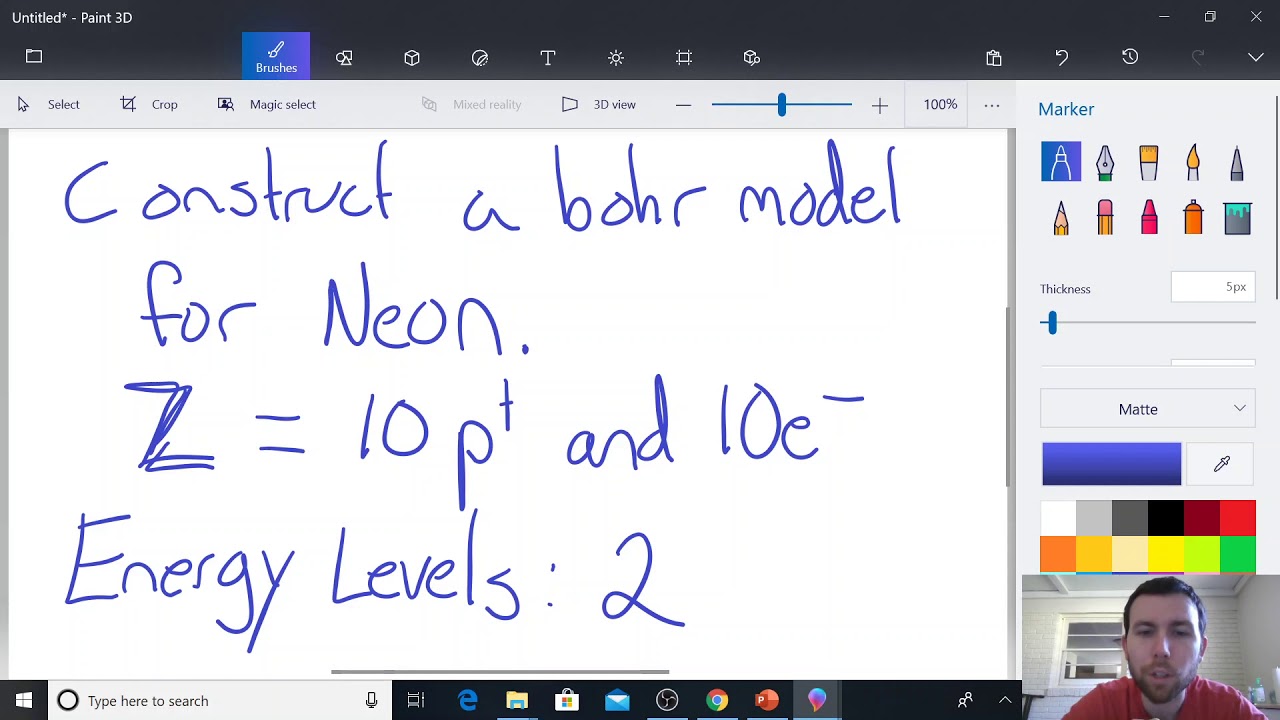
Image taken from the YouTube channel Jackson Kinton _ Staff – EnloeHS , from the video titled Neon Bohr Model Example .
Deconstructing the Neon Bohr Model: A Simple Explanation
To effectively explain the "neon bohr model" to a broad audience, the article layout should follow a logical progression, building understanding from basic principles to a specific visualization. We need to make the abstract concrete and digestible.
Introduction: Setting the Stage for Neon
Begin with a concise introduction that clearly defines the scope of the article. Mention that the Bohr model is a simplified, yet helpful, way to visualize atoms and that the article will specifically focus on understanding how it applies to neon.
- Briefly introduce the concept of atoms and elements.
- Introduce neon as a noble gas with unique properties.
- Clearly state the purpose of the article: to explain the neon Bohr model.
Understanding the Bohr Model: The Foundation
This section lays the groundwork for understanding the neon-specific application. It’s essential to define the Bohr model’s components and limitations before discussing neon.
The Basic Components of the Bohr Model
Explain the fundamental parts of the Bohr model in an easy-to-understand manner. Use visuals here if possible.
- The Nucleus: Explain that it contains protons (positive charge) and neutrons (no charge).
- Electron Shells (Orbits): These are the paths electrons take around the nucleus. Explain they are quantized, meaning electrons can only exist at specific energy levels/distances.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus.
Key Principles of the Bohr Model
This section focuses on the crucial principles that govern the Bohr model.
- Quantized Energy Levels: Electrons can only exist at specific energy levels (orbits).
- Electron Transitions: Electrons can "jump" between energy levels by absorbing or emitting energy. This is the source of light emission.
Limitations of the Bohr Model
Acknowledge that the Bohr model is a simplified representation.
- Mention that it doesn’t perfectly describe all atoms, especially those with many electrons.
- Briefly state that more complex models like the quantum mechanical model exist.
Diving into Neon: Applying the Bohr Model
This section focuses specifically on neon, applying the principles explained earlier.
Neon’s Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Provide concrete numbers for neon.
- Atomic Number: Clearly state neon’s atomic number (10), which means it has 10 protons.
- Number of Neutrons: Mention the most common isotope of neon (Neon-20) has 10 neutrons. Explain what isotopes are.
- Number of Electrons: Explain that a neutral neon atom also has 10 electrons.
Electron Configuration of Neon: Filling the Shells
Explain how neon’s electrons are arranged in the Bohr model. Use a diagram if possible.
- First Shell: Explain that the first shell can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
- Second Shell: Explain that the second shell can hold a maximum of 8 electrons.
- Neon’s Configuration: State that neon has 2 electrons in the first shell and 8 electrons in the second shell (2,8). Emphasize that this makes the second shell full.
Stability of Neon: The Noble Gas Advantage
Explain why neon is a noble gas and its connection to the Bohr model.
- Full Outer Shell: Explain that having a full outer shell (valence shell) makes neon very stable and unreactive.
- Inertness: Explain that this stability is why neon is used in lighting and doesn’t readily form chemical bonds.
Visualizing the Neon Bohr Model: A Clear Diagram
This is a crucial part. Include a simple, clear diagram of the neon Bohr model.
- Labeled Nucleus: Clearly label the nucleus with the number of protons and neutrons.
- Electron Shells: Draw two distinct electron shells.
- Electrons: Place two electrons in the first shell and eight in the second, clearly marking them.
Neon in Action: Real-World Applications
Briefly discuss practical uses of neon.
- Neon Signs: Explain how neon’s emission of light, when excited, is used in neon signs.
- Other Applications: Briefly mention other uses, such as in some types of high-voltage indicators and vacuum tubes.
This structure provides a thorough yet approachable explanation of the neon bohr model, starting with the foundational principles and progressing to specific details and visualizations.
FAQs: Understanding the Neon Bohr Model
Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better grasp the concepts of the Neon Bohr model.
What makes the Neon Bohr Model different from the simple Hydrogen Bohr Model?
The primary difference is that neon, unlike hydrogen, has 10 electrons. The Neon Bohr Model attempts to illustrate how these electrons are arranged in different energy levels or shells around the nucleus. This leads to more complex interactions and energy transitions than in the simpler hydrogen model.
How are electrons arranged in the Neon Bohr Model?
In the Neon Bohr Model, electrons fill the energy levels starting from the innermost shell. The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons, and the second shell can hold up to 8. So for Neon, the first shell has 2 electrons, and the second has 8, completing its outer shell configuration.
Why is the Neon Bohr model important?
Even though it’s a simplified model, the neon bohr model illustrates key concepts of atomic structure, such as quantized energy levels and electron configurations. It’s a stepping stone to understanding more complex atoms and their behavior in chemical reactions.
Is the Neon Bohr Model a completely accurate representation of the neon atom?
No. The Bohr model, including the Neon Bohr model, is a simplified model that’s helpful for initial understanding. It doesn’t account for the wave-like nature of electrons or the more complex quantum mechanical descriptions of atomic structure. It shows how energy levels work, but not the full picture.
And there you have it – the neon borhs modle demystified! Hopefully, this makes understanding of the neon borhs modle a little clearer. Happy learning!