M-Line Striations: What’s Behind Muscle’s Dark Secret?
Muscle physiology presents a complex interplay of structures and processes. The M-line, a critical component within the sarcomere, plays a pivotal role in muscle organization. Myosin filaments, the primary contractile proteins, anchor at this central line, ensuring proper alignment during muscle contraction. Understanding the relationship between the M-line and muscle striations requires careful consideration of techniques like electron microscopy. One key question that arises from observations and studies using these techniques is, is the striation on muscles the m line? Addressing this question demands a nuanced comprehension of sarcomere banding patterns and the distinct contributions of each structure to muscle function.
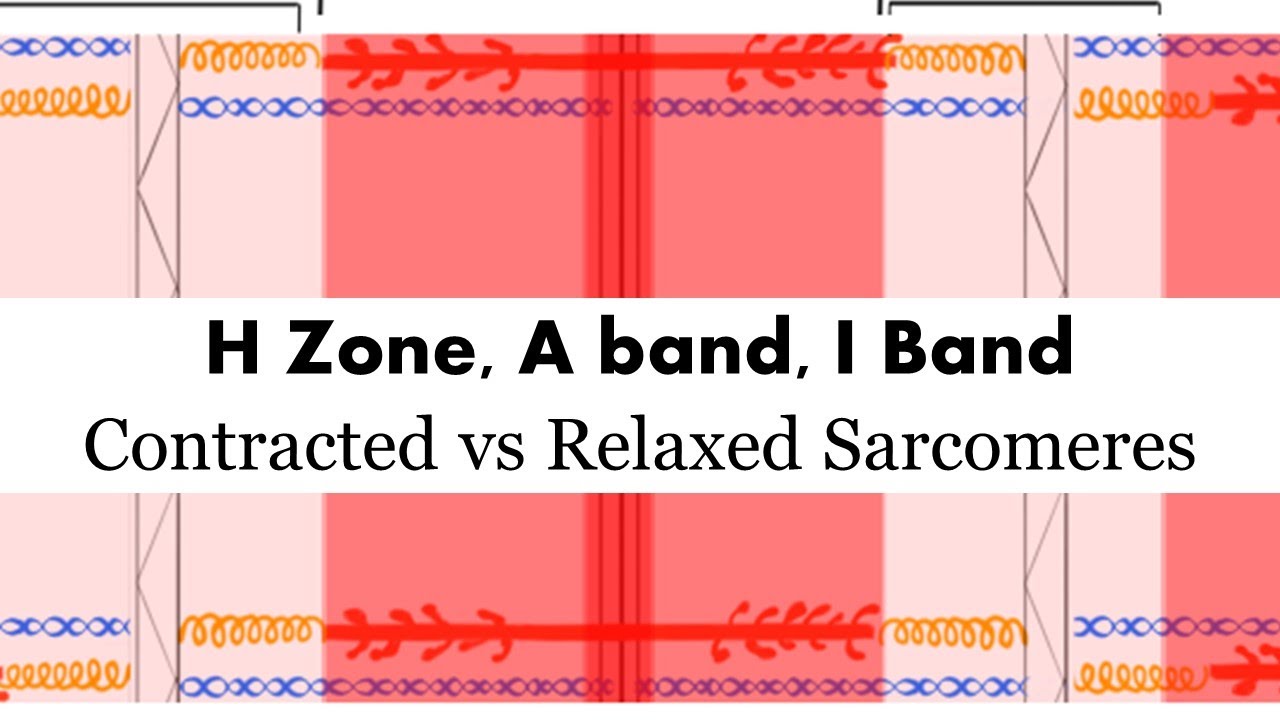
Image taken from the YouTube channel Anatomy Hero , from the video titled Contracted vs Relaxed Sarcomere (H zone, A Band, I Band) .
M-Line Striations: Decoding Muscle’s Structure and the "M-Line" Question
Understanding muscle striations is crucial for grasping how muscles function. When examining skeletal muscle tissue under a microscope, a distinct pattern of light and dark bands becomes visible. These are striations, representing the organized arrangement of proteins within muscle fibers. A key component of this structure is the M-line. Let’s delve into what M-line striations are and answer the core question: Is the striation on muscles the M-line?
Understanding Muscle Striations
Muscle striations are not a single line, but rather a recurring pattern of bands resulting from the arrangement of contractile proteins. These proteins, primarily actin and myosin, are organized into repeating units called sarcomeres.
- Sarcomere: The fundamental functional unit of muscle contraction.
- Z-disc: Defines the boundaries of the sarcomere. Actin filaments are anchored here.
- I-band: A light band containing only actin filaments.
- A-band: A dark band containing both actin and myosin filaments.
- H-zone: A lighter region within the A-band, containing only myosin filaments.
- M-line: A dark line in the middle of the H-zone, holding myosin filaments together.
The M-Line’s Role in Sarcomere Structure
The M-line is a crucial structural component that runs down the center of the sarcomere, bisecting the H-zone. It serves to anchor and align thick filaments (myosin) within the sarcomere.
Composition of the M-Line
The M-line isn’t a single protein structure, but a complex assembly of several proteins, including:
- Myomesin: A major component that links myosin filaments together.
- M-protein (Myosin-binding protein C-like): Contributes to maintaining the structural integrity of the M-line.
- Creatine Kinase (MM-CK): An enzyme involved in energy metabolism, present in high concentrations near the M-line to provide energy for muscle contraction.
Function of the M-Line
The M-line’s primary functions include:
- Stabilizing Myosin Filaments: It acts as a scaffold, preventing the myosin filaments from drifting apart during muscle contraction.
- Maintaining Sarcomere Organization: By holding the myosin filaments in their proper arrangement, it ensures the sarcomere maintains its structural integrity.
- Facilitating Force Transmission: It likely contributes to the efficient transmission of force generated by myosin during muscle contraction.
Answering the Question: Is the Striation on Muscles the M-Line?
No, the striation on muscles is not solely the M-line. The overall striated appearance is due to the alternating arrangement of the entire sarcomere components (A-bands, I-bands, Z-discs, H-zones, and M-lines). The M-line is a component of the sarcomere and contributes to the striated appearance, but it is not the only factor. It represents a distinct dark line within the larger striation pattern.
Think of it like this: a barcode has many black and white lines. The striation on muscles is like the entire barcode pattern, while the M-line is like one specific dark line within that pattern.
The following table summarizes the relationship:
| Feature | Description | Contribution to Striations |
|---|---|---|
| Sarcomere | Repeating unit of muscle contraction | Overall striated pattern |
| A-band | Dark band containing actin and myosin filaments | Dark band in striation |
| I-band | Light band containing only actin filaments | Light band in striation |
| Z-disc | Boundary of sarcomere, anchors actin filaments | Defines sarcomere edges |
| H-zone | Lighter region within the A-band, containing only myosin | Light region within A-band |
| M-line | Anchors myosin filaments in the center of the H-zone | Dark line within H-zone |
In conclusion, the M-line is a critical component of the sarcomere, essential for maintaining its structure and facilitating muscle contraction. While it contributes to the striated appearance of muscle tissue, it is not synonymous with the entire striation pattern. The striations are a result of the organized arrangement of all the components within the sarcomere.
M-Line Striations: Decoding Muscle’s Dark Lines – FAQs
These frequently asked questions help clarify the nature and significance of M-line striations in muscle tissue.
What exactly are M-line striations?
M-line striations are dark lines visible under a microscope in the center of the A-band within a muscle sarcomere. Functionally, they represent the M-line, a structure formed by proteins that hold myosin filaments together. In essence, the striation on muscles is the m line.
Why are M-line striations sometimes referred to as a "dark secret"?
The "dark secret" refers to the diagnostic challenge posed by variations or disruptions in these striations. Changes can indicate various muscle disorders or diseases, yet pinpointing the exact cause isn’t always straightforward.
What can cause abnormalities in M-line striations?
Damage or alterations can stem from several factors, including genetic mutations affecting M-line proteins, certain muscular dystrophies, or even intense exercise-induced muscle damage. It requires careful pathological analysis to differentiate the origin of the changes.
How are M-line striations used in muscle diagnosis?
Muscle biopsies are often examined microscopically. The appearance of M-line striations—their presence, shape, and uniformity—provides crucial clues in diagnosing specific muscle pathologies. Examining how distinct is the striation on muscles to the m line, helps doctors understand the muscle tissue health.
So, did you figure out the ‘dark secret’ behind M-line striations? Hopefully, you now have a much clearer picture of what’s going on in there and how it all relates to the big question: is the striation on muscles the m line. Now go forth and flex those knowledge muscles!